
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- The April Of The Penguin (Pun Intended)
- What Are Spammy Backlinks?
- Types Of Google Penalties
- Common Sources Of Spammy Links
- Residual Spammy Backlinks
- Guest Posts On Low Quality Websites
- Paid Links And Link Exchanges
- Low Quality Press Release Websites
- Link Farms
- Directories
- Forum Spam
- Comment Spam
- Excessive Links From Non-Niche Related Websites
- Backlinks From Websites In Foreign Languages
- Guest Posting At A Scale
- Links From Generally Spammy Websites
- A Note About Outgoing Links
- Step-By-Step Process Of Identifying Spammy Links
- What To Do Once You Have Identified A Spammy Link?
- Conclusion
Introduction
Backlinks are possibly the most talked about, if not the most important aspect of search engine optimization, and for good reason.
When every aspect of on-page SEO is directly under the control of website owners, backlinks and other aspects of off-page SEO are the only thing that truly differentiates websites and enables search engines to rank them.
However, just like with the first draft of anything is bad, the first time backlinks were introduced as a ranking factor, there was a flaw in the logic supporting them.
As soon as website owners realised that such a flaw exists, they started abusing the power of links. This led to the birth of ‘link farms’, websites that existed only to give out backlinks, along with a number of other ‘black hat’ backlink building practices.
Thankfully things changed with Google Penguin Update that was rolled out in 2012.
The April Of The Penguin (Pun Intended)
On April 24th 2012, Google rolled out the Penguin update and changed the way SEO was conducted up until that point. The objective of the algorithm update was quite simple- to put an end to spammy backlink practices.
However, contrary to popular belief, the update does not penalise websites that have spammy backlinks. Instead, it devalues links that originate from ‘spammy’ websites. This means even if your website has a few spammy links, there is a high likelihood that they will not have any influence over your website performance in the search engine result pages (SERPs).
With that said, in some cases, where a website has too many spammy links pointing towards it, Google may devalue all of the links, including the healthy and valuable ones.
What Are Spammy Backlinks?
Simply put, spammy backlinks are links originating from spammy websites.
Such links are usually either coming from low-quality websites that are known from spamming (like link farms) or simply from websites that have poor domain authority.
The traffic coming through these links is usually from countries that you don’t target and can often result in an unusual spike in your website’s traffic.
If you have noticed similar activity on your website, chances are that you have at least a few spammy backlinks pointing to your website.
Let’s understand their possible sources:
Types Of Google Penalties
Google’s link related penalties are of two types: manual penalty and algorithmic penalty. Let’s look at what they entail in a bit more detail:
Link Penalty 1: Manual Link Penalty
As the name suggests, a link penalty that has been initiated after a manual review of your backlink profile by someone in Google’s webspam team.
In most cases, manual reviews are triggered by one of the three following reasons:
- The Google algorithm may have detected a red flag in your backlink profile and as a result of that, marked your backlink profile for a manual review.
- You may be operating in a competitive niche where a lot of players have been known to use black hat technique to improve their rankings. Such niches are constantly and closely monitored by Google’s webspam team.
- A spam report by a user or a competitor can also trigger a manual review of your backlink profile.
Besides these reasons, another reason behind a manual review can be pure bad luck. Google’s webspam team is tasked with randomly checking various backlink profiles to ensure there is no link spam taking place.
When you are hit with a manual penalty, you will be notified by Google via the Google Search Console. Manual link penalty notifications usually feature a subject line similar to “notice of unnatural links detected to website.com”.
However, sometimes, a similar notification may be used by Google to simply tell you that they have noticed unnatural links in your backlink profile and that you should get rid of them before you are hit with a penalty.
If you have received a penalty, the terms “manual penalty” will definitely be a part of Google’s communication.
Link Penalty 2: Algorithmic Link Spam Penalty
As mentioned earlier, Google’s Penguin algorithm update has been programmed to automatically detect instances of unnatural backlinks. Website penalties triggered as a result of the Penguin link filter of Google are known as algorithmic penalties.
Unlike in the case of manual penalties, Google doesn’t usually send out notifications regarding algorithmic penalties.
With that said, if your website has been hit with an algorithmic penalty, you will not need a notification from Google to be sure. Most penalties are followed by a sharp and sudden drop in organic traffic.
In some extreme cases, your website may be completely de-indexed, completely wiping off any organic traffic from your website. Now that we have discussed the different link related penalties that Google gives out, let’s look at the link building tactics that cause such penalties.
Common Sources Of Spammy Links
As mentioned earlier, spammy backlinks usually originate from spammy websites. If you find that term vague, here are a few possible places where your website’s spammy backlinks live or originate from:
1. Residual Spammy Backlinks
If your website has existed since before the Penguin update, there is a chance that you or whoever was managing your SEO at the time may have unknowingly secured some spammy links.
2. Guest Posts On Low Quality Websites
Guest posting is perhaps one of the most well-known tactics for building quality backlinks. However, when you are guest posting often, things can become grey without warning. You may find yourself creating low quality links either unknowingly, or because you are a beginner that just got a taste of a traffic spike from a backlink.
Whatever the case may be, you must absolutely avoid the following when you are looking for guest posting opportunities:
- Blog Networks: Blog networks are websites that give out backlinks to paying members. Google hates these websites and for good reason. The easiest way to spot a blog network is to look at their guest posting guidelines. If they include rigid word count rules and similarly rigid rules about words to link ratios, it is best for you to avoid such a website. Most good blogs don’t care whether you are writing only 400-600 words or have included links in the introduction of your article.
- Article Websites: Article websites are quite similar to blog networks with the major difference being that you can pay for every article that you publish. Most articles on these websites are written with backlinking as an objective and thus, usually lack quality. While links from these websites don’t usually hurt your website’s SERP performance, they will also not add any positive value, Google has made sure of that.
- Web 2.0 Blogs: Also known as single post blogs, these are one or two page websites that are usually created on WordPress subdomains. Just like links from article websites, links from single post blogs don’t add any value towards improving the SERP visibility of your website.
3. Paid Links And Link Exchanges
Posting on article websites and blog networks is not the only way to purchase links on the web. A much ‘safer’ way is to purchase links from a variety of different websites.
However, this process involves multiple steps (content production, outreach, negotiation, and payment) and is often dependent on multiple individuals that usually don’t work for you.
For instance, you have no control on the activities of the website you purchase a link from. Similarly, if you are using an external partner to secure paid links, you cannot truly ensure that they are doing it in an inconspicuous manner.
While Google doesn’t yet have a bulletproof way to detect paid links, some such links are easier to spot than the others. When Google does find out that a website has been engaging in paid link building, the search engine giant is known to impose heavy penalties.
The risk with purchasing links is that it is not necessary for someone on your team to mess up and negatively affect your website’s rankings. Anyone involved in the process, including websites that sell links and middlemen that help you secure links can screw up and the repercussions can trickle down to your website.
In other words, it is possible to purchase links ‘safely’ but it requires you to trust a bunch of strangers (in most cases).
The case is even more risky when it comes to exchanging links through link schemes as there are several more people involved in such schemes. If you are engaged in a link exchange scheme, remember that even if one person slips up, there is a good chance that your website may attract a penalty.
4. Low Quality Press Release Websites
Getting links from press release websites is another popular way to secure genuinely valuable links. However, not all news websites work in the same way.
The ones that genuinely have the kind of reputation that can benefit your website often have stringent quality and information verification standards. These standards are often so stringent that they discourage link spammers.
It is always easier for spammers to reach out to low quality news websites that don’t ask for sources of information or high quality content. Moreover, it is easier for spammers to convince these websites that a website redesign of an unknown business or brand is newsworthy.
However, the links you get from low-quality press syndication are often not indexed or hold no real SEO value. This means that while this tactic may not result in a website penalty, the time and effort you expend in securing such links will not result in any benefits for your website.
5. Link Farms
We have already spoken about how links from link farms have been devalued by Google.
In some cases, getting backlinks from link farms may even result in short term SEO gains but using such websites is definitely not a sustainable or ethical way to build backlinks.
6. Directories
Backlinks from business directories have been a point of debate for quite some time. This is because there are high quality directories like Yelp that follow strict quality standards. On the other hand, there are also business directories that exist only to give out backlinks.
As a result, Google has decided to devalue links from certain business directories. Another reason for directory links to offer little to no benefits is the high number of outgoing links that directories have. This means that the ‘link juice’ is actually being divided among all the outgoing links. For instance, if you get a link from a directory that has 1000 outgoing links, then the value of the link juice for you would be 1/1000.
Google’s Matt Cutts has outlined a few considerations that you can ask in order to determine if a link from a certain business directory will be beneficial for your website. These are:
- Check how many submissions does the directory reject. If just about anyone can get a listing on the directory, there’s a good chance that the links will not give you any benefit.
- Check the quality of websites whose submissions are accepted by the directory. If most of the websites look spammy, it is best to move on to finding better business directories.
- In many cases, even genuine directory websites will charge a fee and it’s not wrong. However, in the case of genuine business directories, this fee is usually used to compensate the directory’s team for the time and effort it takes to verify submissions from businesses.
When you consider the above standards for directory listings, you will end up eliminating most of the directories that you may have been considering. That’s a good thing. There is afterall, no benefit of getting a backlink from a directory that Google has deindexed.
7. Forum Spam
As an SEO beginner, getting links from forums may seem like a ‘hidden opportunity’ but it is actually far from even being a legin opportunity to get a backlink.
The logic is simple. Forums, much like social media websites, have very little control over the quality of links being posted on them by the users. Just about anyone can get a backlink from a forum.
For this reason, Google has deindexed links coming from most forums. Once again, this means that while these links will not hurt your website’s SEO results, they won’t contribute to them either.
8. Comment Spam
Blog commenting used to be a popular link building strategy up until a few years ago. The reason for this popularity was simple- it is incredibly easy to get a backlink from an unmoderated comment section.
However, the catch is, most unmoderated comment sections have hundreds, sometimes thousands of outgoing links.
Moreover, most websites that have unmoderated comment sections are usually low-quality websites.
These two reasons together mean that getting links from unmoderated comment sections is probably not a good idea.
Now that we know where spammy links originate, you can actively work towards avoiding them.
However, as mentioned earlier, there’s a chance that your website already has a few spammy backlinks pointing towards it. Even if you have been walking on the straight and narrow and have never used a blackhat SEO technique, you may have attracted certain backlinks because of negative SEO practices done by some unethical competitors.
Let’s see how you can identify them and prevent them from hurting your website’s SEO results.
9. Excessive Links From Non-Niche Related Websites
In many cases, you may benefit from a backlink from an unrelated website. For instance, a link from your local NGO’s website or from a local government authority website will result in SEO benefits regardless of whether their niche is related to yours or not.
However, the examples mentioned above are perhaps the only cases where a link from a website that has nothing to do without a niche will not hurt the results of your SEO efforts.
The most commonly made mistake in this respect happens when websites start securing reciprocal links. Such link swaps, where you link to someone’s website and they link to you, make almost perfect sense in the case of niche related websites. Just like your website is expected to attract backlinks from others’ websites, it is natural that you will link to them.
However, when such reciprocal links are noticed between websites that are not related to each other, Google treats it as unnatural link building and may end up hitting you with a penalty.
10. Backlinks From Websites In Foreign Languages
If your website is in the English language, Google will expect most links to come from other websites that use the same language.
An exception to this rule can be in the case where a business website is serving users in a different country. However, even in such cases, Google will expect your website to get links from websites that use the same language as the people who make up most of your online audience. Meaning, if most of your audience is in France and your website or business is in the UK, Google will expect you to get links from websites in French and in English.
If your website has backlinks from a website that uses, say, Japanese, it will take notice and assume that something fishy is going on. If Google’s algorithms notice several links coming from such websites, it will start devaluing the links in your backlink profile.
11. Guest Posting At A Scale
As mentioned earlier, guest posting is an excellent way to secure some great, authority enhancing backlinks for your website, but only when done correctly.
Looking at how excellent a backlink building strategy guest posting is, some businesses tend to go overboard with it. Meaning, they only focus on the numbers and often overlook the quality of the content they are producing or the websites they are working with.
This often happens when businesses enlist the help of low quality guest posting services.
To avoid getting your website de-indexed or your backlinks devalued, make sure you are only guest posting on niche related, high authority websites with (mostly) branded anchors. Don’t focus on numbers or on building links using exact match anchor texts.
If you are consistent with your efforts, Google will take notice and you will, in turn, notice an improvement in your organic traffic numbers.
12. Links From Generally Spammy Websites
So far, we have discussed a variety of spammy websites including link farms, low quality business directories, and link exchange networks.
However, there are a couple of other types of spammy websites like porn websites and gambling websites. Don’t get me wrong, if you have a website that operates in one of those niches (I hear they are incredibly profitable), getting backlinks from other similar websites will make a lot of sense.
However, if you have a ‘legitimate’ business, you must ensure you are not attracting (or even giving out) links from such websites.
A Note About Outgoing Links
Don’t let all this talk about inbound links make you think that outgoing links are bad or that you have to show some kind of restraint while placing outgoing links on your own website.
As mentioned earlier, if Google expects your website to get links from other websites, it also expects other websites to get links from yours. By this logic, you should feel no hesitation while giving backlinks to other websites when they deserve them.
Even if we ignore that logic, outbound links are an important part of ethical SEO.
How?
For one, placing an outbound link to a high authority website will help you get noticed by them and may even help you start a relationship that helps you secure links from said high authority website.
With that said, there are a handful of easy to follow guidelines that you should keep in mind while placing outbound links on your website:
- Avoid adding outgoing links to websites from which you would not want incoming backlinks. This includes ‘spammy’ websites, non niche websites, and foreign language websites. Besides these, make sure you are using your own judgement to gauge the quality of a website that you may be considering linking to.
- If you are placing outgoing affiliate links on your website, make sure that you associate them with a ‘no-follow- attribute.
- Don’t go out of your way to hide outbound links.
- If your website hosts user generated content, make sure you are taking out the time to give no-follow attributes to all links in user generated content.
- Periodically go through your outbound links profile and make sure that there are no broken links. Broken outbound links are associated with poor user experience and may result in poor search engine performance.
Step-By-Step Process Of Identifying Spammy Links
Identifying spammy backlinks on your website is actually a surprisingly straightforward process:
Step 1: The first step is to run your website through an SEO tool’s backlink checker. I personally use Ahrefs for this purpose as the tool offers all the information I need to root out the bad backlinks from virtually any backlink profile.
Step 2: The tool will then display the details of the entire backlink profile of your website. Something like this:
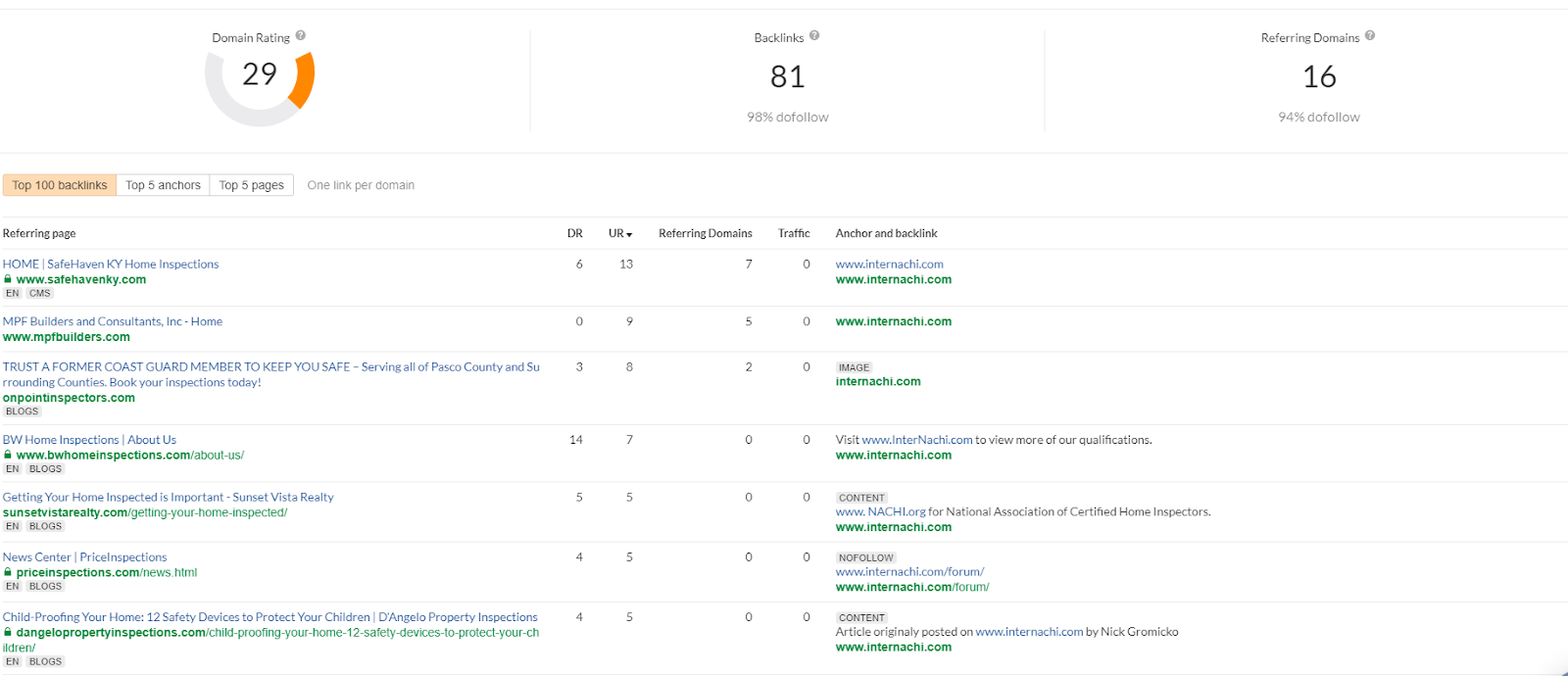
Here, you have to locate websites and domains with a low Domain Rating (DR) score.
Step 3: Low DR score is a good indicator of spammy websites but it isn’t foolproof. This is because websites with low DR scores may simply be new websites. This is why, once you have identified, you have to conduct further investigation. Usually, other signs of a spammy website include origins from a foreign website that you don’t target or websites that clearly don’t belong to your niche. Spammy sounding domains are also a clear giveaway. Another way to identify a spammy backlink is to check the anchor text. If the text is in a foreign language or simply not related to your niche, there is a strong chance that the backlink is not good for your website.
If you have executed the above steps correctly, now you must have a list of spammy backlinks pointing to your website.
What To Do Once You Have Identified A Spammy Link?
Once you have identified the spammy links, it is time to take steps to get rid of them. While some may say that asking Google to disavow those links is the only way forward, that’s actually not good advice.
Even Google advises against using their link disavow unless it is an extreme case. Before we see how disavowing a link works, let’s also look at a couple of alternatives:
- Request The Website Owner/Manager To Remove The LinkIn most cases, you will find the contact details of the website owner on the website itself. If this is available, send them a (polite) email asking them to remove the link to your website.With that said, this step rarely works but it is a requirement that Google needs you to fulfill before you ask them to disavow a link from a website.
- Request The Hosting Company To Remove The LinkIf you don’t hear back from the website’s owners, you can also reach out to their hosting providers with a request to remove the backlink to your website.To look up who is hosting the website in question, you can use this service that is literally called WhoIsHostingThis.The service will also provide you with the contact details of the hosting provider.
- Submit A Disavow Request To GoogleTo submit a request to Google to disavow a link to your website is simply asking them to ignore it. Google offers a tool that will help you do this.It allows you to submit a text file containing all the spammy links that you want them to ignore.Once you have submitted a disavow request, all that is left to do is wait. Processing your request will take a few weeks.During this time, keep a close watch on your rankings to notice subtle improvements that will gradually become apparent as your disavow request is processed.
Conclusion
Spammy backlinks can originate from a number of sources and sometimes, having spammy backlinks pointing to your website is not even your fault. However, in the eyes of the search engine, spammy links are associated with a spammy website.
This is why, regularly checking your website’s backlink profile to identify spammy backlinks and removing them is a necessary task. Luckily, thanks to SEO tools like RankWatch, the task, when done regularly, will not demand a lot of time or effort. The little bit of time that you will have to spend on identifying and removing spammy backlinks is a small price to pay to ensure your website’s performance in search results doesn’t get affected.
Got more questions about spammy backlinks? Or did I forget to mention a source of spammy backlinks that you have discovered?
Whatever it is, feel free to share with me (and all the readers) in the comment section below.



